Starting the blog on a good note- the second quarter of 2023 celebrated a record low of only 34% of victims paying off to ransomware attackers. This decline is due to the propagation of cybersecurity practices, which encouraged companies to educate their employees on red signs and invest in adequate tools and software.
Now, to talk about Business Email Compromise or BEC attacks, we can’t overlook how email fraud is damaging the global economy with the loss of billions of dollars and tarnished business reputation!
So, to improve how you respond and mitigate BEC attacks directed towards your company, we are sharing a 6-step strategy to outwit hackers.
A Real-life Example!
We aren’t straightaway jumping to the 6-step strategy because we want to scare (or rather aware) you first!
As a reader, you may not be aware of how badly the repercussions of a BEC attack can reflect on your company and its profits. If an employee falls for a fraudulent email message sent by a hacker impersonating a CXO and ends up sharing confidential files, transferring money, or doing whatever action they mentioned in the email, your business would become so susceptible.
They can take away a large chunk of money, expose some of your not-so-legal operations, share data on the dark web, victimize your employees and customers, and whatnot!
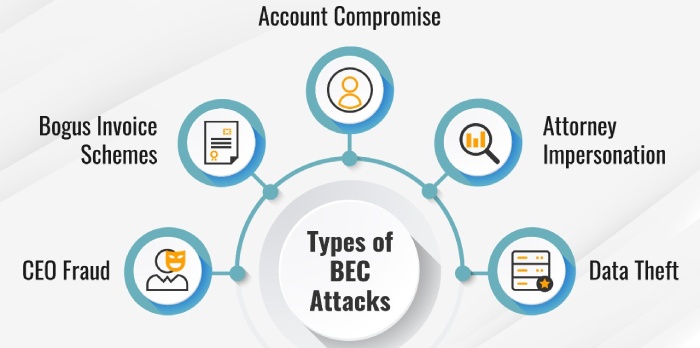
Image sourced from fortinet.com
From 2013 to 2015, the tech giants Google and Facebook collectively lost $121 million to a series of BEC attacks. So, what happened was that a Lithuanian hacker, who goes by the name Evaldas Rimasauskas, started sending counterfeit invoices in the name of a Taiwanese computer hardware company ‘Quanta Computer.’ He kept sending fake invoices for computer parts that the companies never purchased until the matter came out, and he was sentenced!
That’s exactly why all companies should invest in cybersecurity tools and training programs with regular mock drills, irrespective of their size and scope of expansion.
6-Step Strategy To Combat Business Email Compromise Attacks
Threat actors usually look for money or data they can sell on the dark web or to your competitors in exchange for money; in either case, the ultimate goal is to make money. For a successful BEC attack, all they have to do is convince the recipient that they are actually who they are claiming to be, and the task (sharing data, transferring money, etc.) has to be done urgently. What’s worse is that hackers are now using AI tools like ChatGPT to create refined phishing emails with no grammatical or spelling mistakes, underlining the need for companies to be vigilant, proactive, and technically sound.
So, here’s how a 6-step strategy unfolds.
1. Email Authentication Protocols
Threat actors mostly buy a domain name similar to your official domain name with minor spelling changes that usually go unnoticed by recipients. For example, using vv instead of w, or 0 instead of o.
However, sometimes hackers don’t buy a new domain and instead link a new email address with your company’s official domain. So, if you have SPF, DKIM, and DMARC in place, emails coming from unlisted email addresses will be marked as suspicious, and your employees will be less likely to fall into the trap.
2. Employee Training
Let your employees know the red flags of a fake email and a way to respond and report them. Moreover, the reported emails should be logged and traced back to their original IP address to catch the culprit.
Ask them to double-check the sender’s and reply-to email addresses and do not show urgency for unreasonable requests. We recommend taking confirmation over a voice call before transferring a big amount or sharing sensitive details.

On the other hand, employees (including CXOs and top management position holders) should also be trained to refrain from displaying irritation or anger when team members reach out to verify requests. Such negative reactions could deter them from adopting this safety precaution.
3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security beyond the traditional username and password by requiring users to authenticate their identity through multiple verification methods, such as passwords, biometrics, or authentication codes.
This multi-layered approach significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if login credentials are compromised. Cybercriminals often exploit weak or stolen passwords, making MFA an effective deterrent against such attempts. Additionally, MFA enhances the company’s overall security posture, safeguarding sensitive data, confidential information, and proprietary systems.
The implementation of MFA reflects a proactive and robust cybersecurity strategy, providing a resilient barrier against evolving cyber threats and enhancing the overall resilience of the company’s digital infrastructure.
4. Strong Security Policies
Clear policies and procedures should be in place for financial transactions and access to confidential data. This includes putting limit caps, approvals, and verification of changes to payment information.
Also, make it a practice to levy fines on the ones who don’t abide by these policies so as to maintain strictness and stringency.
5. Ditch Legacy System
Older computer systems, known as legacy systems, can unintentionally invite cyberattacks. These systems use outdated security measures and may lack support for modern cybersecurity tools, making them more prone to exploitation.
Their software is often outdated, making it easier for attackers to take advantage of vulnerabilities without critical security updates. Also, these systems may not work well with advanced security features like multi-factor authentication and integration with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, increasing the risk of unauthorized access.
The reluctance to upgrade or replace these legacy systems worsens BEC attack risks, as organizations may struggle to fix inherent design issues and respond effectively to new threats.
6. Trace Back Emails to Their Original IP Addresses
You can trace back email to reach the culprit by accessing the full email header and carefully scrutinizing its routing information and email metadata. This is a simple and quick process, and tools like MXToolBox Email Header Analyzer, Messageheader by Google, and WhatIsMyIPAddress are helpful in the reverse DNS lookup.

In conclusion, curtailing BEC attacks demands unwavering vigilance, continuous training, and investment in advanced tools. A significant part of this strategy is ensuring email security with the Sender Policy Framework (SPF), and this includes the practical implementation of Automatic SPF flattening. This integrated approach forms a robust defense against such pervasive cyber threats. Carelessness can cost you millions of dollars and a reputational setback.